Autonomous Vehicles – The next-generation connected vehicles
My Father always chose to stay at a house close to my school so that I don’t have to travel a long distance to reach school from home. Having a car allowed us to change our lifestyle, it allowed us to live further away from our jobs and school, stay at a house that had plenty of space to run around, and explore new communities.
But this automobile revolution also created all sorts of problems such as parking space and traffic. Wouldn’t it be better if you are given a choice before a revolution happens whether to be a part of it or not? Well, you have a chance now!
The next revolution is the autonomous vehicle (AV) or the self-driving car. I did some research about AV technology, how it works, and some secondary effects.
What is an autonomous vehicle?
An autonomous or self-driving vehicle is a vehicle that can sense the surrounding environment and function without any human involvement. Yes, you guessed it right, these are driverless vehicles. You don’t have to be on the driver’s seat and control the steering, switch gears, or even apply the brakes. You can go anywhere and do everything that you do with a traditional vehicle.
Levels of automation
According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), there are six levels of automation for driving extending from completely manual (0) to fully automatic (5). Let me give an overview of all the levels:
- Level 0 or no automation: You must be on the driver’s seat, and you have complete control over the vehicle regarding steering, gears, braking, acceleration, and power.
- Level 1 or single feature automation: This is the first level of automation. The vehicle can assist the driver with at least one automatic feature. Cruise control is a good example of first-level automation, it helps to maintain a safe distance between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you on the road.
- Level 2 or multiple feature automation: The vehicle can assist the driver with at least two automatic features such as lane centering and cruise control.
- Level 3 or partial self-driving automation: The vehicle can sense environmental changes and take over full control of the car. But the vehicle still needs the driver to be alert and prepared to take over if the autonomous system is unable to complete the job.
- Level 4 or complete automation: The vehicle does not require any human intervention in most cases. However, you still have an option to override and take controls manually.
- Level 5 or self-driving automation vehicles: The vehicle does not require any human intervention and there is no option for the driver to switch to manual controls. In fact, the vehicle will not have any steering, braking, or acceleration pedals.
How do autonomous vehicles work?
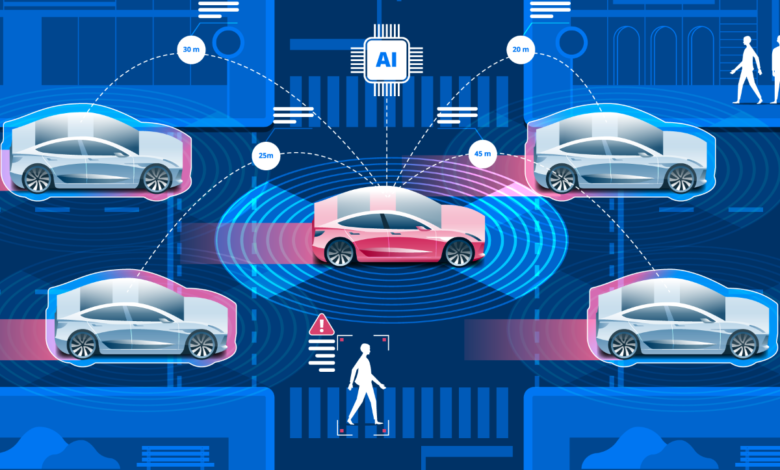
Self-driving cars do not require a driver to get from point A to B. The technology used in and on the vehicle is the driver. This technology makes use of many sensors such as camera sensors, ultrasonic, radar, and lidar sensors. The sensors are placed at the back and front of the vehicle. Some of the cameras and lidar sensors are located on the roof that acts as eyes for the vehicle. Lidar sensors are like radar sensors, but they detect light rays reflected by the surroundings and the objects instead of radio waves. Lidar sensors help the autonomous vehicle to detect the objects in the surroundings.
However, lidar cannot detect the traffic signs on the road. Cameras are used to detect traffic signs, lanes, and obstacles. Cameras and lidar sensors cannot detect fog, so radar sensors are used in case of fog to avoid collisions. The GPS provides the accurate location of the vehicles with the help of highly efficient digital maps.
All data from the sensors are accumulated and processed in one or more processors. Some manufacturers like NVIDIA and AMD provide processing chips for autonomous vehicles.
Challenges with autonomous vehicles
Radar and Lidar: Both lidar and radar use signals and frequencies to interpret the surrounding objects and obstacles. When many autonomous vehicles run on the same street, the frequencies and signals might interfere with each other. Lidar is also not very cost-effective.
Climatic changes: Autonomous vehicles are still not tested for dangerous weather conditions like heavy rainfall, heavy fog, and blurred vision. The cameras and sensors will not be very helpful to identify a lane covered in snow or markings disrupted by water.
Traffic rules: How will autonomous vehicles handle bumper-to-bumper traffic and bottlenecks? Are they going to follow a special lane? I mean we are still going to have regular cars on the road for the next 20 years, at least.
Legal responsibility for accidents: We cannot rule out accidents. And when they happen, who is going to be held responsible, the passenger, the manufacturer, car owner, or the vehicle technology? I mean there won’t be any option to even take manual control of fully autonomous vehicles.
Expensive: Autonomous vehicles use a lot of hardware and software devices to operate and process the incoming data. All this comes with a price. They will always be more expensive than traditional cars.
Benefits of autonomous vehicles

As autonomous vehicles grow towards becoming a more realistic model of transportation, there are a lot of exciting new possibilities that they can bring. Let’s look at some of the pros:
- Less number of accidents due to human errors like a distraction, poor driving, and impaired decision making.
- Autonomous vehicles will have a faster reaction time and ability to communicate with other autonomous vehicles which will help to reduce traffic.
- Since you don’t have to drive your car, you use the commute time to do other productive work like reading, writing, completing your official work, and attending meetings. You can even sleep if your commute time is very long.
- Parking will be easier; your car will drop you at your destination and find a suitable spot for parking itself.
Final Verdict
The future of autonomous vehicle technology is uncertain, but whether you like it or not the revolution of driverless cars is bound to transform the transportation industry in one way or another. Like I said in the beginning, it’s up to you whether you want to be a part of it or not.



